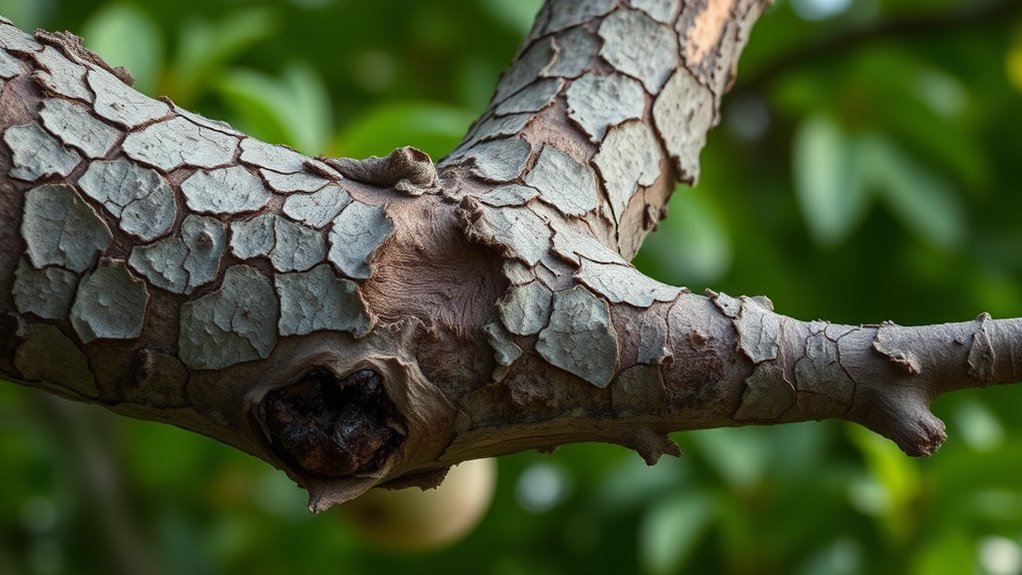
To distinguish canker diseases on branches, look for sunken, discolored lesions with clear margins that gradually expand over time. These lesions often cause bark cracking or dieback around the affected area. Unlike physical damage, canker signs are characterized by irregular, sunken spots that worsen and have distinct edges. Pay attention to progression—if lesions grow and life-like tissue appears compromised, you’re likely dealing with canker. Keep exploring for detailed ways to identify and manage these infections.
Key Takeaways
- Look for sunken, discolored, or irregularly shaped patches on branches with distinct margin edges.
- Observe if lesions are expanding over time, causing bark cracking or dieback.
- Differentiate canker from physical damage by examining lesion pattern and progression.
- Check for small lesions that enlarge and lead to bark separation or cracking.
- Monitor for associated symptoms like branch dieback or sudden bark discolors indicating infection.
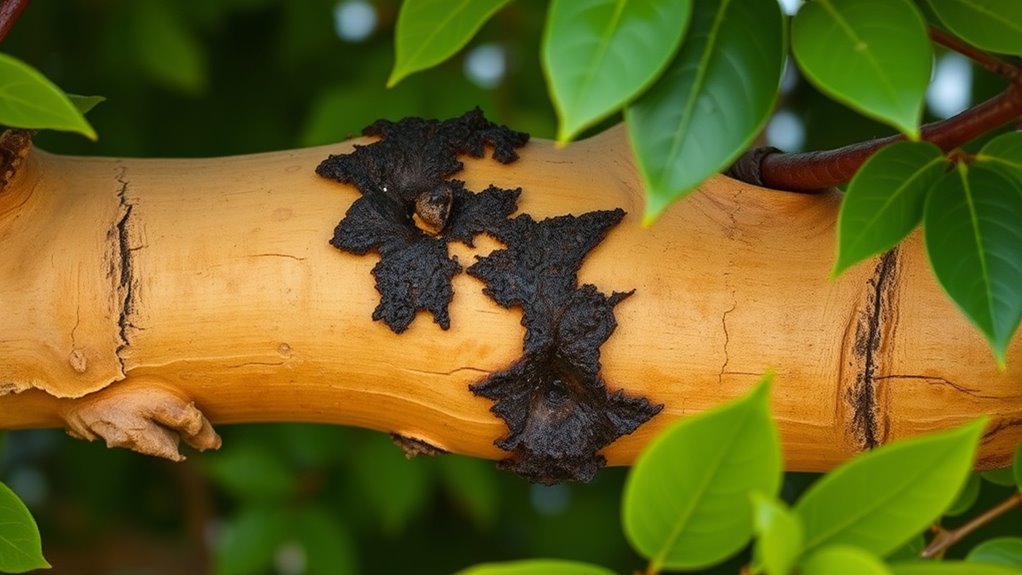

Canker diseases can be tricky to identify because their symptoms often resemble those of other tree health issues. When examining your trees, you might notice some irregularities on the branches, such as sunken or discolored areas, but these signs can easily be mistaken for physical damage or other infections. To accurately distinguish canker diseases, it’s essential to look closely at the pattern and progression of the symptoms. Typically, you’ll see lesions that start small but expand over time, causing the bark to crack or die back. These lesions often appear as sunken, discolored patches with a distinct margin separating healthy tissue from infected areas.
Canker symptoms include sunken, discolored patches with expanding lesions and distinct margins.
One key to managing canker diseases effectively is to focus on wound management. Any physical damage—such as pruning cuts, broken branches, or injuries from storms—creates entry points for the pathogens responsible for cankers. Proper wound management involves making clean cuts with sharp tools and sealing or promptly treating large wounds to prevent pathogen entry. Avoid leaving open cuts or wounds exposed, as these become vulnerable spots where the disease can establish itself and spread further along the branch or into the trunk. Regularly inspecting your trees and trimming damaged or dead branches helps reduce the risk of infection and supports healthy growth.
Disease prevention plays an essential role in keeping canker diseases at bay. You can do this by maintaining overall tree health through proper watering, mulching, and fertilization, which strengthens the tree’s natural defenses. Avoid injuring the branches unnecessarily during pruning; always prune during dry weather and sterilize your tools between cuts to prevent spreading pathogens. Additionally, keep an eye on your trees for early signs of infection—such as small, discolored spots or areas of dieback—and address issues promptly before they escalate.
Implementing good hygiene practices is also fundamental. Dispose of infected plant material properly, and avoid moving infected wood from one location to another, as this can spread the disease. Regularly inspecting and maintaining your trees minimizes weak spots and reduces the likelihood of pathogen invasion. If you do notice signs of canker, it’s best to act quickly—remove and destroy infected branches, and consider consulting an arborist for advanced measures. Through vigilant wound management and proactive disease prevention, you can protect your trees from the damaging effects of canker diseases and promote their long-term health and robustness.
Being aware of Louisiana Alimony Laws and how they influence post-divorce support can also help you plan for long-term stability and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Prevent Canker Diseases on My Trees?
To prevent canker diseases on your trees, you should use proper pruning techniques to remove infected or dead branches, which helps reduce disease spread. Additionally, choose disease-resistant varieties suited to your climate. Keep your trees healthy by watering and fertilizing appropriately, and avoid injuries during maintenance. Regular inspections help catch issues early, and maintaining good sanitation minimizes the risk of canker pathogens taking hold.
Are Certain Tree Species More Susceptible to Canker Diseases?
Did you know that some species, like maples and oaks, are more susceptible to canker diseases? You’ll find that species susceptibility varies, with certain trees showing less disease resistance. If you plant less vulnerable species, you reduce your risk of infection. Understanding which trees are more prone helps you make informed choices to protect your landscape, ensuring healthier, more resilient trees over time.
What Are the Environmental Factors That Promote Canker Development?
You should know that environmental factors like high soil moisture and excessive sun exposure promote canker development. When soil stays too wet, it weakens your tree’s defenses, making it more vulnerable to infections. Conversely, too much sun can stress the tree, creating openings for pathogens. Maintaining balanced soil moisture and providing adequate shade can help reduce the risk of cankers forming and spreading on your trees.
Can Canker Diseases Spread Between Different Types of Plants?
Think of canker diseases as sneaky invaders that can cross species boundaries like a traveler crossing borders. Yes, they can spread between different types of plants through cross species transmission, especially if the plants’ immune responses are weak or compromised. When an infected plant’s defenses falter, it’s easier for the disease to hop to new hosts, turning your garden into a battleground where pathogens find new opportunities to thrive.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Untreated Canker Infections?
If you leave a canker infection untreated, it can seriously harm your tree’s health over time. As the disease progresses, it weakens branches and trunk tissues, increasing the risk of branch dieback and eventual tree death. You might notice increased vulnerability to other pests and diseases, which further endangers your tree’s long-term well-being. Acting promptly helps prevent extensive damage and preserves the tree’s robustness.
Conclusion
By observing the symptoms, identifying the signs, and understanding the differences, you can effectively distinguish canker diseases on branches. Recognize the telltale signs, note the pattern of bark lesions, and compare the affected areas. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and act promptly. With careful attention, you can prevent spread, protect your trees, and ensure healthy growth. Remember, knowledge is your best tool in managing canker diseases on branches.