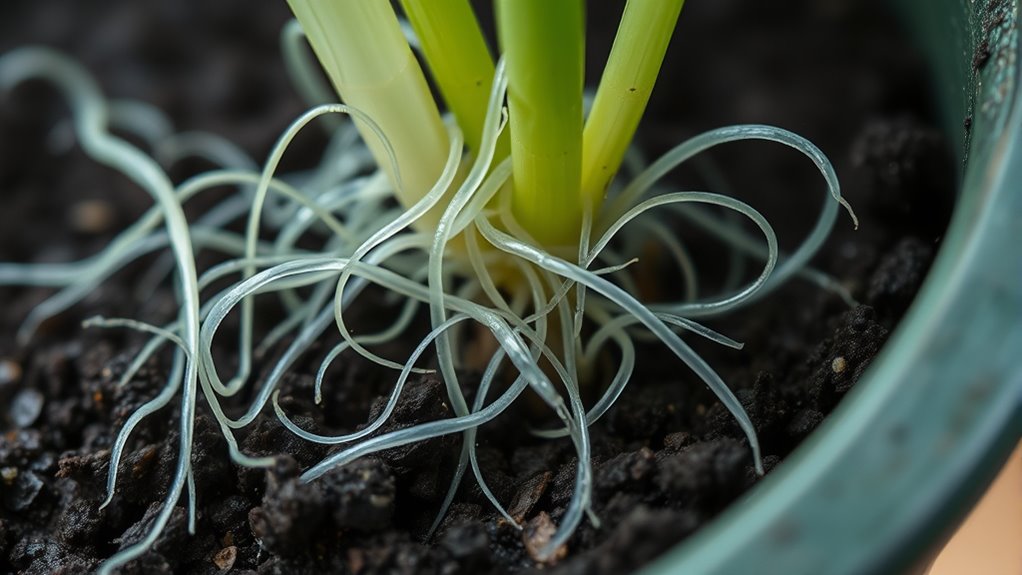
To identify root-feeding nematodes in potted plants, look for signs like wilting, yellowing leaves, or stunted growth, and examine the roots for galls, knots, or lesions. Carefully inspect soil and roots for tiny, whitish, or translucent worms. Using a microscope, you can recognize specific nematode types by their shape and features. Accurate diagnosis is essential, and knowing more about these signs will help you effectively manage the problem.
Key Takeaways
- Examine roots for galls, knots, lesions, or discoloration indicative of nematode infestation.
- Use microscopic analysis to identify nematode morphology, focusing on size, shape, and specialized features.
- Collect soil and root samples for laboratory testing and microscopic examination.
- Differentiate nematode species through morphological traits and, if needed, molecular diagnostic techniques.
- Observe plant symptoms such as wilting and yellowing alongside root abnormalities to support accurate identification.
Recognizing Symptoms of Nematode Infestation
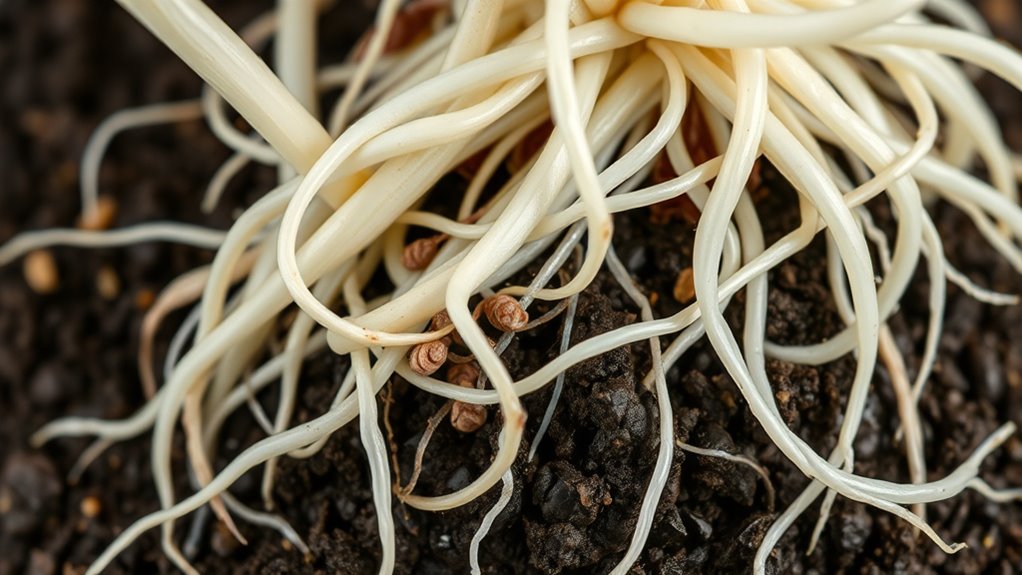

Nematode infestations often go unnoticed until they cause significant damage, but recognizing early symptoms can help you take prompt action. One of the first signs is visible signs of plant stress, such as wilting, yellowing leaves, or stunted growth, despite proper watering and care. You might also notice uneven or poor development of roots when inspecting your potted plant. These symptoms indicate that pests could be interfering with nutrient uptake. To manage the problem, implement pest management strategies like removing affected plants, soil treatment with nematicides, or introducing beneficial nematodes. Understanding how contrast ratio influences image quality can aid in diagnosing issues related to visual clarity and color rendering in affected plants. Early detection is vital to prevent widespread damage and ensure your plant’s health, so regularly monitor for these signs and act quickly if you notice any unusual stress symptoms.
Common Types of Root-Feeding Nematodes in Potted Plants
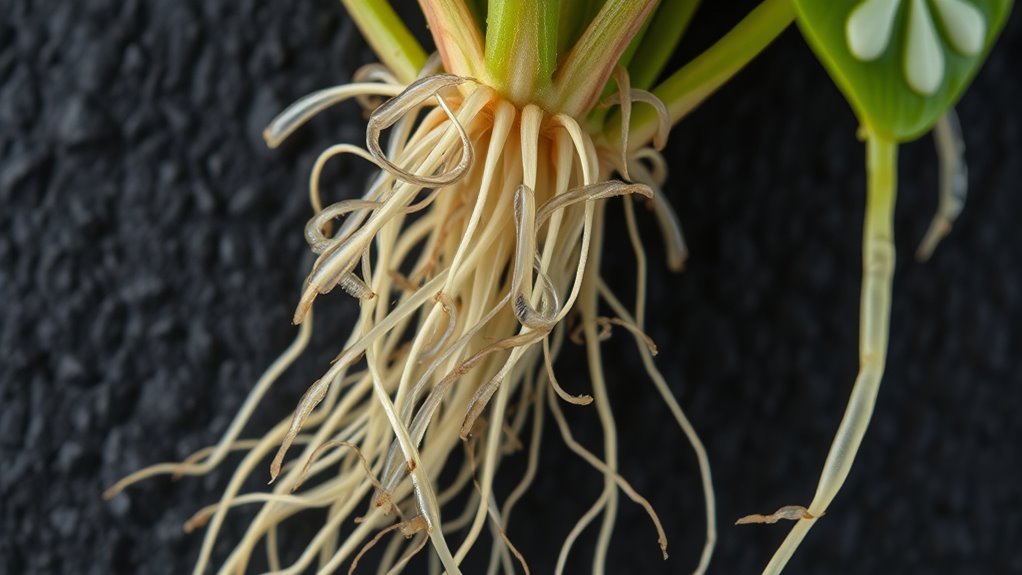

Several common types of root-feeding nematodes can attack potted plants, each causing distinct damage and requiring specific management strategies. The most prevalent include root-knot nematodes, dagger nematodes, and cyst nematodes. These pests have different Nematode life cycles, influencing how quickly they reproduce and spread. Root-knot nematodes create galls that distort roots, while dagger nematodes feed on root tissues, weakening the plant. Cyst nematodes form protective cysts, making them harder to control. Effective management often involves biological control, such as introducing natural predators or beneficial fungi. Recognizing these types guarantees you can implement targeted strategies to limit damage and reduce reliance on chemical controls. Understanding their life cycle and behavior is key to managing these persistent pests. Understanding their behavior helps in developing more effective control methods.
Examining Roots for Nematode Presence
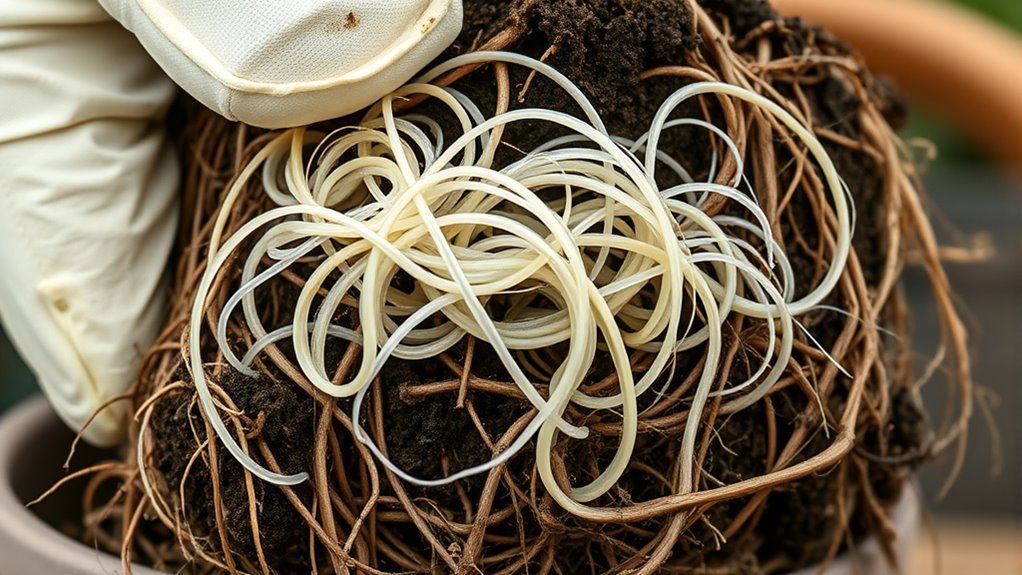

To determine if your potted plant is infested with root-feeding nematodes, start by carefully removing the plant from its container and gently brushing away excess soil from the roots. Look closely for visible signs like galls, knots, or lesions. You can also take soil samples near the roots for nematode trapping—using methods like placing a baited trap in the soil to attract these pests. Examine the roots for tiny, white or translucent nematodes moving among the root tissues. Here’s a visual to help you identify potential nematode presence:
| Root Signs | Soil Sampling & Trapping |
|---|---|
| Galls or knots | Use nematode traps in soil |
| Root lesions | Collect soil for analysis |
| Discolored roots | Look for nematode movement |
| Root decay | Conduct soil sampling |
| Abnormal root growth | Detect nematodes with traps |
Additionally, understanding the vibrational energy within the soil environment can help identify pest activity, as it influences nematode movement and behavior.
Microscopic Identification Techniques
Using a microscope is vital for accurately identifying root-feeding nematodes, as many are too small to see with the naked eye. Microscopic techniques help distinguish species based on morphological features, shape, and size. To enhance visibility, staining techniques are often employed to highlight internal and external structures, making identification easier. Electron microscopy offers detailed images at a cellular level, revealing features invisible under light microscopes. Proper identification is crucial for implementing effective control strategies and preventing crop damage. Key methods include: – Applying specific stains to differentiate nematodes from plant tissue – Using electron microscopy for high-resolution imaging – Examining morphological features like stylet shape and cuticle structure These techniques enable precise identification, which is essential for targeted management of nematode infestations in potted plants.
Differentiating Nematode Damage From Other Problems

You need to recognize whether plant problems come from nematodes or other issues. Look for specific visual symptoms like stunted growth or yellowing leaves. Checking roots and soil can help you distinguish nematode damage from pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies. Utilizing AI-powered analysis can assist in identifying subtle signs of nematode infestation for more accurate diagnosis.
Visual Symptom Indicators
Since root-feeding nematodes often cause subtle underground damage, their effects on plants can be difficult to distinguish from other problems. Look for visual symptom indicators that signal issues with plant health, such as:
- Yellowing or wilting leaves despite proper watering
- Stunted growth or overall poor vigor
- Unusual root deformities or galls
These signs can mimic nutrient deficiencies or other pests, so it’s essential to use diagnostic tools to confirm nematode presence. While visual cues provide initial clues, they aren’t definitive. Combining observations with soil or root tests enhances accuracy in identifying root-feeding nematodes, ensuring you can take targeted action to protect your plants. Recognizing these symptoms early can save your plants from further decline. Top-rated anime movies can also serve as a relaxing way to unwind during plant care routines.
Soil and Root Checks
To accurately identify root-feeding nematodes, examining soil and roots directly is essential, as their damage can resemble other issues like nutrient deficiencies or fungal infections. Start with soil testing to detect nematode presence and population levels. Carefully inspect roots for signs such as galls, lesions, or abnormal swelling, which are typical of nematode activity. Conduct plant tissue analysis to identify nutrient imbalances that might mimic nematode damage. Comparing symptoms from soil and root checks helps differentiate nematode injury from other problems. If you find suspicious root abnormalities and soil test results confirm nematodes, you can confidently diagnose nematode damage. This targeted approach ensures you’re addressing the actual cause rather than misdiagnosing other issues. Using vetted testing methods can improve the accuracy of your diagnosis and lead to more effective management strategies.
Tips for Accurate Diagnosis and Confirmation
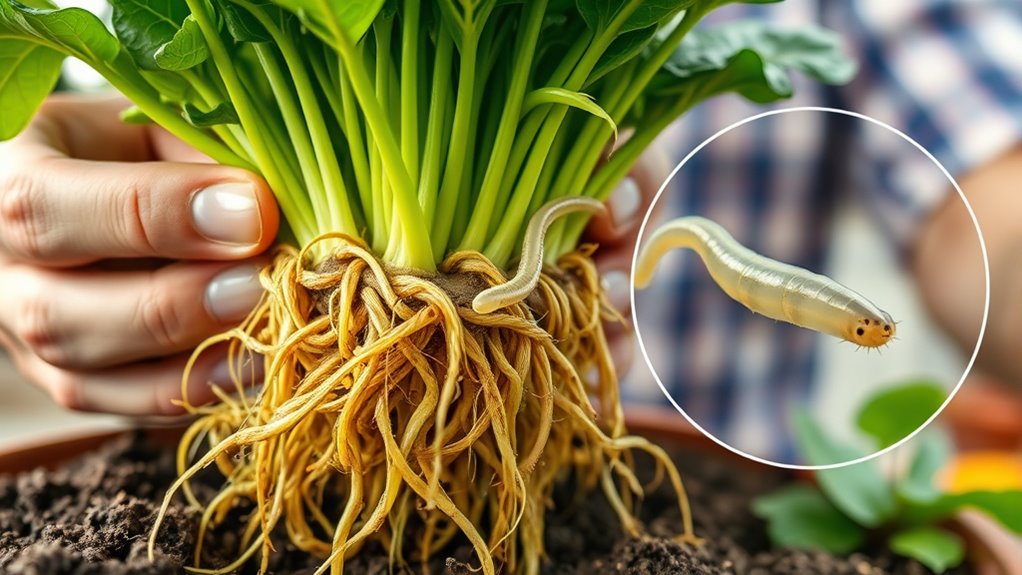

Accurate diagnosis of root-feeding nematodes relies on careful sampling and identification techniques. To improve your chances, consider examining multiple root samples and using a microscope for detailed observation. Confirm your findings with laboratory identification if possible. Using nematode resistant cultivars can prevent future issues, but proper diagnosis ensures targeted control. Incorporate biological control methods, such as beneficial nematodes, to manage infestations naturally. To enhance your accuracy, keep these tips in mind: proper sampling methods — collecting samples from various plants and root zones, using a high-quality microscope for detailed examination, and cross-referencing with lab identification for confirmation. Following these steps helps you distinguish between different nematode species and verify your diagnosis, leading to effective management strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Nematodes Spread Between Potted Plants?
You might wonder how nematodes spread between potted plants. They often hitch a ride on contaminated tools, pots, or even plant material. To prevent this, practice plant quarantine when introducing new plants, and regularly soil sterilization helps eliminate nematodes. Avoid sharing soil or plants with others without proper checks. Maintaining clean tools and containers minimizes the risk of spreading these tiny pests between your potted plants.
Can Nematode Infestations Occur Without Visible Root Damage?
Think of nematodes as secret agents working undercover. Even if you don’t see visible root damage, hidden symptoms like stunted growth or yellowing leaves can signal their presence. Nematode detection isn’t always straightforward; infestations can occur without obvious signs. You need to stay vigilant, as these tiny invaders often hide in your plants’ roots, making early detection challenging but essential to prevent further damage.
Are There Specific Soil Treatments Effective Against Root-Feeding Nematodes?
You can effectively manage root-feeding nematodes with specific soil treatments. Soil fumigation using chemical agents helps eliminate nematodes, but it requires careful application and safety precautions. Biological controls, like beneficial nematodes or predatory fungi, offer eco-friendly options that target nematodes naturally. Combining these methods can improve your chances of controlling infestations and protecting your potted plants from further damage.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Nematodes on Plant Health?
You might notice that nematodes can weaken your plants over time, negatively affecting plant vigor and reducing crop yield. Their root damage hampers water and nutrient uptake, leading to stunted growth and increased vulnerability to other pests and diseases. Long-term nematode infestations can cause sustained health issues, making it harder for your plants to thrive and ultimately decreasing your harvest or overall plant quality.
How Often Should I Inspect My Potted Plants for Nematodes?
You should inspect your potted plants regularly—at least every 4 to 6 weeks—to catch nematodes early. Consistent inspection frequency helps you identify signs of infestation before severe damage occurs. Look for stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or unusual root deformities. Early detection is key to managing nematodes effectively, so make these inspections a routine part of your plant care to keep your plants healthy and thriving.
Conclusion
By spotting the subtle signs beneath the surface, you hold the key to safeguarding your plants’ future. Think of each healthy root as a fortress, and nematodes as hidden invaders trying to breach it. With keen observation and careful diagnosis, you become the guardian of your potted garden’s essential. Remember, uncovering these tiny threats today guarantees your plants flourish tomorrow—trust your instincts and stay vigilant in the battle beneath the soil.









